Resistor Colour Code of learn.
HOW TO REMEMBER THE COLOUR CODE
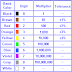
Resistance colour value
black 0
brown 1
red 2
orange 3
yellow 4
green 5
blue 6
violet 7
gray 8
white 9
silver -2
gold -1
Here are some common ways to remember the colour code:
Resistance is measured in OHMs.
Resistors have RESISTANCE and the main purpose of a resistor is to reduce the CURRENT FLOW.
"Ohm." but this symbol is not available on some word-processors, so the letter "R" is used.
The letter "E" is also sometimes used and both mean "Ohms."
A one-ohm resistor is written "1R" or "1E." It can also be written "1R0" or "1E0."
A resistor of one-tenth of an ohm is written "0R1" or "0E1."
The letter takes the place of the decimal point.
10 ohms = 10R
100 ohms = 100R
1,000 ohms = 1k (k= kilo = one thousand)
10,000 ohms = 10k
100,000 ohms = 100k
1,000,000 ohms = 1M (M = MEG = one million)
Every resistor is identified by colour bands on the body, but when the resistor is a surface-mount device, numbers are used and sometimes letters.
You MUST learn the colour code for resistors.
Reading 4-band resistors.
The most "common" type of resistor has 4 bands and is called the 10% resistor.
It now has a tolerance of 5% but is still called the "10% type" as the colours increase by 20% so that a resistor can be 10% higher or 10% lower than a particular value and all the resistors produced in a batch can be used.
The first 3 bands produce the resistance and the fourth band is the "tolerance" band. Gold = 5%
(Silver =10% but no modern resistors are 10%!! - they are 5% 2% or 1%
Read more ...
HOW TO REMEMBER THE COLOUR CODE
Resistance colour value
black 0
brown 1
red 2
orange 3
yellow 4
green 5
blue 6
violet 7
gray 8
white 9
silver -2
gold -1
Here are some common ways to remember the colour code:
Resistance is measured in OHMs.
Resistors have RESISTANCE and the main purpose of a resistor is to reduce the CURRENT FLOW.
"Ohm." but this symbol is not available on some word-processors, so the letter "R" is used.
The letter "E" is also sometimes used and both mean "Ohms."
A one-ohm resistor is written "1R" or "1E." It can also be written "1R0" or "1E0."
A resistor of one-tenth of an ohm is written "0R1" or "0E1."
The letter takes the place of the decimal point.
10 ohms = 10R
100 ohms = 100R
1,000 ohms = 1k (k= kilo = one thousand)
10,000 ohms = 10k
100,000 ohms = 100k
1,000,000 ohms = 1M (M = MEG = one million)
Every resistor is identified by colour bands on the body, but when the resistor is a surface-mount device, numbers are used and sometimes letters.
You MUST learn the colour code for resistors.
Reading 4-band resistors.
The most "common" type of resistor has 4 bands and is called the 10% resistor.
It now has a tolerance of 5% but is still called the "10% type" as the colours increase by 20% so that a resistor can be 10% higher or 10% lower than a particular value and all the resistors produced in a batch can be used.
The first 3 bands produce the resistance and the fourth band is the "tolerance" band. Gold = 5%
(Silver =10% but no modern resistors are 10%!! - they are 5% 2% or 1%